A) the number of births equals the number of deaths.
B) each couple has an average of two children which also results in zero population growth.
C) each couple has an average of two children, but may still allow for population growth.
D) the population reaches carrying capacity.
E) all of the adult population is married.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The maximum per capita rate of increase for a population that can occur under ideal conditions is the
A) population growth.
B) biotic potential.
C) environmental resistance.
D) carrying capacity.
E) doubling time.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which term describes the concept that no two species can have the same "job" in the community at the same time?
A) competitive exclusion
B) habitat
C) niche
D) mimicry
E) symbiosis
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a true statement?
A) The growth rate can be positive and a population can still be the same size year after year.
B) The growth rate has to be zero before a population can be the same size year after year.
C) Replacement reproduction automatically gives a growth rate of zero.
D) A growth rate of zero means the population is dying.
E) The growth rate can be negative and a population can still be the same size year after year.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider that a species of salmon lays 20,000 eggs per pair when it spawns and dies.At the end of five years,an average of one pair of mature salmon from this group of hatched eggs returns again to spawn in the parent stream (19,998 have died) .What is the per capita rate of increase?
A) 10,000, because there were that many eggs produced per parent fish (r)
B) 2,000, because this must be divided by five years
C) zero, because there is exact replacement of the previous generation
D) -2,000, because there was this much average die-off per year
E) -19,998, because there was this much total loss
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Population growth rate would be negative when
A) birthrate is greater than death rate.
B) death rate is greater than birth rate.
C) all couples are married but average less than two children apiece.
D) a country becomes poorer, because it is related to economic growth.
E) better health care reduces the death rate and increases survivorship of newborns.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An ecosystem contains
A) only the biotic (living) components of the environment.
B) only the abiotic (nonliving) components of the environment.
C) only the energy flow components of an environment.
D) both the living organisms and the abiotic components of the environment.
E) only the food relationships found in an environment.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a population of 10000 organisms over a one year period there are 750 births and 130 deaths.Calculate the growth rate for that year.
A) 0.062
B) 0.055
C) 0.088
D) 0.013
E) 0.075
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A population age structure in which the birthrate is less than the death rate and the post-reproductive group is the largest would be best represented by a graph with a(n)
A) bell shape.
B) urn shape.
C) pyramid shape.
D) S-shaped curve.
E) J-shaped curve.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A population of 100 butterflies living on an acre of land loses three quarters of its members when a sudden freeze in the spring occurs just after they emerge as caterpillars.This population has undergone a reduction in population size due to
A) An intrinsic factor
B) A density independent control
C) A density dependent control
D) Natural selection
E) An opportunistic control
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A population of 1000 mice living in a barn of land loses one half of its members when a sudden a virus spreads through the population.This population has undergone a reduction in population size due to
A) An intrinsic factor
B) A density independent control
C) A density dependent control
D) Natural selection
E) An opportunistic control
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The theory that plants cannot grow on a particular area until the soil has been developed enough by an earlier community is the
A) climax-pattern model.
B) facilitation model.
C) inhibition model.
D) tolerance model.
E) soil development model.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT an anti-predator defense mechanism?
A) Plant chemicals, including coffee and tea caffeine, make caterpillars sick or jittery.
B) The large eyespots on a moth's wing are exposed abruptly to startle a hungry bird.
C) Many trees, vines, and shrubs have stems lines with long thorns.
D) Prairie dog towns always have several prairie "watchdogs" to alert them of approaching hawks and snakes.
E) Many plants have brightly colored fruit and flowers.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are on vacation in the Canadian Rocky Mountains and you observe that a massive forest fire has burned all the trees off the side of the mountain and sterilized the soil,leaving no topsoil.The type of succession that occurs following this type of fire is
A) secondary succession.
B) pioneer species growth.
C) primary succession.
D) primary soil leaching.
E) facilitated succession.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Overall,the most scientifically correct viewpoint toward predators is
A) predators help keep prey populations from overexploiting limited food resources.
B) generally, ecosystems support more and healthier populations when the large carnivores were eliminated from the system.
C) there is a high level of cruelty and indiscriminate killing among larger predators.
D) when we eliminate predators that could harm us and our activities, we also improve conditions for other animal populations.
E) predators are a neutral influence on prey populations and our activities merely substitute us for the prey we eliminate.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
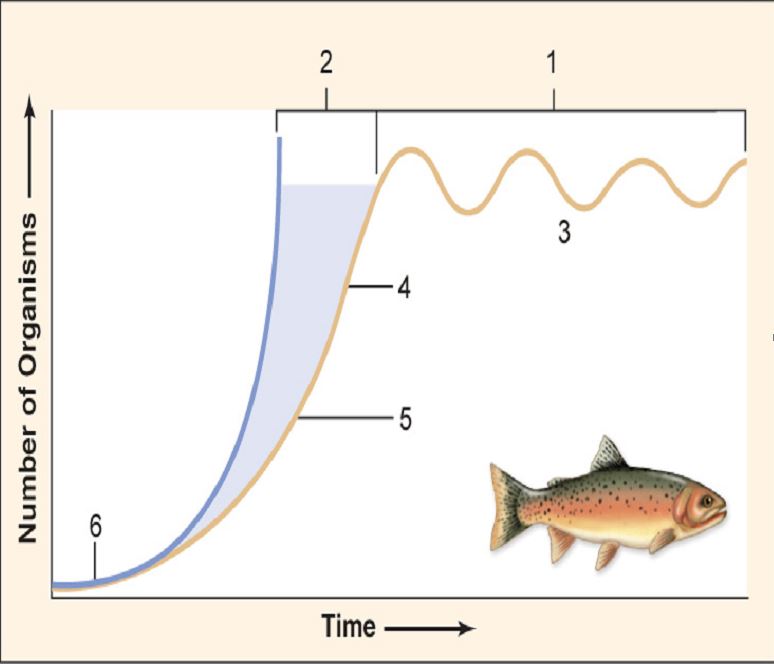 -In Figure 34.03,the biotic potential of the population occurs at number
-In Figure 34.03,the biotic potential of the population occurs at number
A) 1.
B) 2.
C) 3.
D) 4.
E) 5.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There are several species of grain beetles that can live on dry meal obtaining water mostly as metabolic water.Many of these beetle species are grain pests that do considerable damage to stored grain.You set up a dozen jars of dry meal and introduce fifty individuals of each species to each jar,being careful to have half of each species from each sex.The food supply is sufficient to last for a year and the size is adequate so that wastes do not become toxic.Most likely,examination of the jars in six months will find
A) a totally random variation in numbers of both beetles.
B) only one species per jar, similar to the classic experiment with paramecia.
C) the same ratio of beetles as when you started about half from each species.
D) only dead beetles in all jars due to intense competition for the niche.
E) half the jars with more of one species and the other half of the jars will have more of a second species of beetle.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The harmless orange-and-black viceroy butterfly closely resembling the toxic orange-and-black monarch butterfly is an example of
A) Müllerian mimicry.
B) Batesian mimicry.
C) both Müllerian and Batesian mimicry.
D) a case of resource partitioning.
E) a case of competitive exclusion.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A number of populations of different species interacting with one another in a natural environment,such as a rotten log,is called
A) competition.
B) a community.
C) a biome.
D) predation.
E) symbiosis.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Secondary succession will start with bare ground that is lacking any type of soil.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 90
Related Exams