A) an envelope
B) None of these answer options are correct, because viruses have all of these structures.
C) organelles
D) genetic material
E) a protein coat
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Treating a bacterial infection by inoculating the host with a bacterial virus is
A) chemotherapy.
B) phage therapy.
C) None of the answer choices are correct.
D) radiation therapy.
E) antibiotic therapy.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A vaccine against the influenza virus would result in production of antibodies against which of the following?
A) proteins in the envelope
B) the protein coat
C) lipids in the envelope
D) viral DNA
E) viral RNA
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following diseases is not caused by viruses?
A) the common cold and influenza
B) aids and warts
C) diabetes
D) polio and rabies
E) smallpox and mononucleosis
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Oral infections with herpes simplex virus 1 can lie dormant in nerve cells for years.When a patient becomes stressed,the virus is released,forming cold sores on the lips.While lying dormant,the virus is in which of the following states?
A) infective
B) latent
C) replicative
D) symptomatic
E) lytic
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The enzyme that HIV uses to copy its RNA into DNA is
A) reverse transcriptase.
B) RNA polymerase.
C) RNA integrase.
D) DNA polymerase.
E) transcriptase.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer: 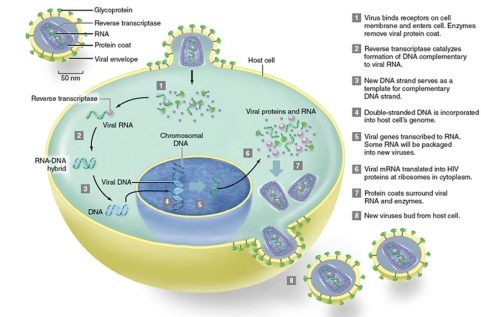 -Based on the figure,which of the following is true of HIV?
-Based on the figure,which of the following is true of HIV?
A) It is an enveloped virus.
B) It replicates in the nucleus of cells.
C) It contains DNA as its genetic material.
D) It uses reverse transcriptase from the cell to make DNA.
E) It lyses cells when it is released.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Many viruses are inhibited by antibiotics.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A layer of membrane outside the protein coat of some viruses is called a(n)
A) capsid.
B) protein coat.
C) envelope.
D) capsomere.
E) plasmid.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The host range of a virus is
A) the type of organisms or cells that a virus can infect.
B) the geographical location in which the virus is found.
C) limited by availability of its needed nutritional resources.
D) always limited to one species.
E) the boundaries of the ecosystem in which it is found.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In studies designed to determine the origin of HIV,how did the researchers first know that Marilyn the chimp may be infected with HIV?
A) She had HIV DNA in her tissues.
B) She had tested positive antibodies against HIV.
C) She had been used in HIV research.
D) She had HIV RNA in her blood.
E) She had symptoms of HIV infection, or AIDS.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The site,in nature,where viruses exist before they infect humans,is the
A) capsid.
B) reservoir.
C) clade.
D) bacteriophage.
E) progenote.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer: 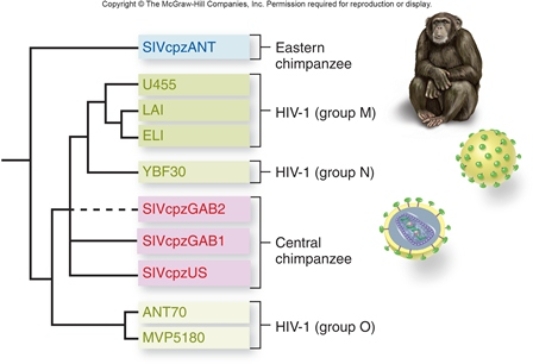 -Based on the figure,which of the following statements is most likely accurate?
-Based on the figure,which of the following statements is most likely accurate?
A) HIV arose more than once.
B) HIV and SIV are not genetically related.
C) SIV only arose once.
D) HIV groups M, N, and O will be more similar to each other than to SIV.
E) The SIV strains will all have more sequence similarity with each other than with any of the HIV groups.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An infectious protein is a
A) prion.
B) virion.
C) virus.
D) prophage.
E) viroid.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Smallpox is an enveloped virus with a DNA genome.We have eliminated this once deadly virus through an aggressive worldwide vaccination program.Why might a vaccine be successful with smallpox,but not with HIV?
A) Host cells have RNA in them, and thus do not raise antibodies against RNA.
B) Viruses with DNA genomes must replicate inside a host cell.
C) Smallpox is an enveloped virus.
D) RNA is more stable than DNA, and is less likely to be destroyed by the vaccine.
E) DNA genomes mutate less rapidly than RNA genomes.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An infectious RNA molecule is a
A) virion.
B) prion.
C) viroid.
D) virus.
E) bacteriophage.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A friend of yours,as a biology major,has prepared microscope specimens from a rat that had been found dead for unknown reasons.Viewing the prepared slide with a light microscope,your friend points out many small round objects,each about 1/10th the diameter of the nearby rat cells,identifying those round objects as viruses,the likely reason for the rat's death.You can interpret from the observations that
A) the viruses your friend identified were likely received as an infection from another organism.
B) these are more likely bacteria, being too large for viruses.
C) they are indeed viruses, likely received from another organism, and are also specifically common bacteriophages.
D) they are probably specialized bacteriophages that commonly infect mammals.
E) they are capsids, which have evolved as a transition between viruses and bacteria.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer:
Five different virus species are shown and labeled arrows indicate structures. 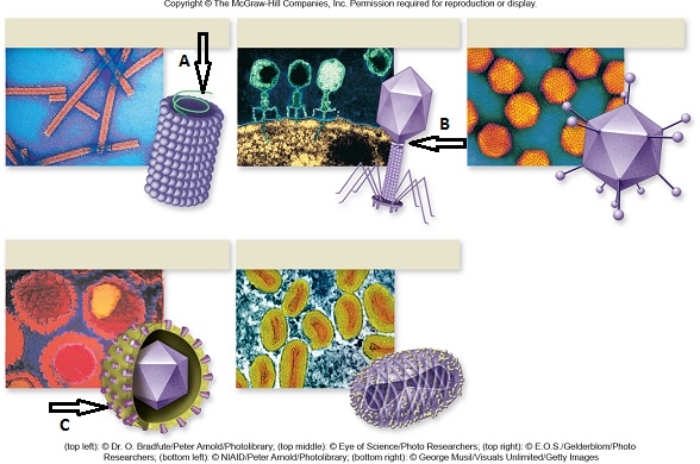 -The virus structure indicated by the arrow labeled C is the
-The virus structure indicated by the arrow labeled C is the
A) genetic material, DNA or RNA.
B) the bacteriophage.
C) the bacterial membrane.
D) the lipid-rich envelope.
E) the protein coat, or capsid.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A trait that is not shared by lytic and lysogenic viruses is
A) lysis of the host cell occurs soon after the infection.
B) a protein capsid specialized for attachment to the host cells.
C) dependence on the metabolism and synthesis processes of the host cell for replication.
D) None of the answer options are correct; lytic and lysogenic viruses share all these listed traits.
E) DNA or RNA is the nucleic acid responsible for storage of the genetic information.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer:  -SIV causes symptomless infections in monkeys and apes,yet causes AIDS-like disease in chimpanzees.HIV is closely related to SIV and causes AIDS in humans.Which of the following is the best explanation for these observations?
-SIV causes symptomless infections in monkeys and apes,yet causes AIDS-like disease in chimpanzees.HIV is closely related to SIV and causes AIDS in humans.Which of the following is the best explanation for these observations?
A) SIV is most likely lytic in apes and monkeys.
B) SIV is most likely latent in chimpanzees.
C) Chimpanzees and humans have a more recent common ancestor.
D) The effects of viruses on different species is random.
E) Monkeys, apes, and chimpanzees are all genetically very similar.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 59
Related Exams