A) 96 utils
B) 108 utils
C) 72 utils
D) 142 utils
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
With a fixed money income, an increase in the price of one good and a decrease in the price of the other will cause the new budget line to intersect the original budget line.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the total utility from consuming the fifth unit of a product is 6 and the total utility from all five units is 162, then the total utility from consuming four units must be
A) 168.
B) 27.
C) 156.
D) 972.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
With diminishing marginal utility, if a consumer reduces her consumption of a good, then her marginal utility from that good would increase.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following has been a significant factor in the ability of iPads to compete effectively against laptop and desktop computers?
A) iPads are often superior to laptop and desktop computers in their ability to create content.
B) A scarcity of production capacity has curtailed the manufacture of laptop and desktop computers.
C) Many consumers perceive that iPads are superior to laptops and desktop computers for the consumption of digital media.
D) The prices of laptops and desktop computers have increased dramatically.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Many people do not steal or commit fraud because to them, the resulting feelings of guilt and uneasiness make the
A) marginal utility of the act increase.
B) marginal utility of the act decrease.
C) marginal cost of the act increase.
D) marginal cost of the act decrease.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal rate of substitution measures the
A) magnitude of the substitution effect.
B) total utility received by a consumer when equilibrium is achieved.
C) extra utility that a consumer derives from successive units of a product.
D) consumer's willingness to substitute one product for another so that total utility will remain constant.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An indifference curve
A) may be either upsloping or downsloping, depending on whether the two products are complements or substitutes.
B) is downsloping and convex to the origin.
C) is upsloping and has a constant slope.
D) is downsloping and concave to the origin.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the diagram. The marginal utility of the third unit of X is 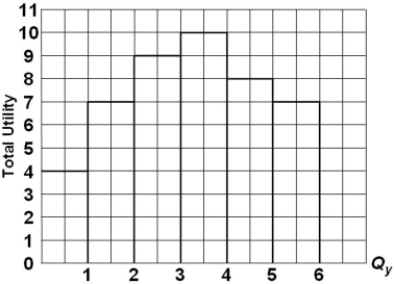
A) 5.
B) 4.
C) 2.
D) 15.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Indifference curves are convex to the origin due to diminishing marginal rates of substitution.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most economists contend that
A) noncash gifts are more efficient than cash gifts.
B) noncash gifts are less efficient than cash gifts.
C) noncash and cash gifts are equally efficient.
D) government can assess consumer preferences better than can consumers themselves.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If total utility is increasing, then marginal utility
A) must be declining.
B) must be increasing.
C) must be increasing at an increasing rate.
D) may either be increasing or decreasing, but it must be greater than zero.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diamond-water paradox arises because
A) essential goods may be cheap, while nonessential goods may be expensive.
B) the marginal utility of certain products increases, rather than diminishes.
C) essential goods are always higher priced than nonessential goods.
D) we sometimes fail to use money as a standard of value.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consumer is making purchases of products Alpha and Beta such that the marginal utility of product Alpha is 30 and the marginal utility of product Beta is 40. The price of product Alpha is $5, and the price of product Beta is $10. The utility-maximizing rule suggests that, to stay within a given budget constraint, this consumer should
A) increase consumption of product Beta and decrease consumption of product Alpha.
B) increase consumption of product Beta and increase consumption of product Alpha.
C) increase consumption of product Alpha and decrease consumption of product Beta.
D) makeno change in the consumption of Alpha or Beta.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Answer the question based on the table below showing the marginal utility schedules for product X and product Y for a hypothetical consumer. The price of product X is $4, and the price of product Y is $2. The income of the consumer is $30.
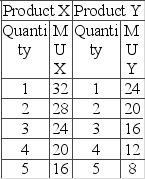 What would be the utility-maximizing combination of products X and Y that could be purchased with $30?
What would be the utility-maximizing combination of products X and Y that could be purchased with $30?
A) 3X and 3Y
B) 4X and 4Y
C) 5X and 4Y
D) 5X and 5Y
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Total utility may be determined by
A) multiplying the marginal utility of the last unit consumed by the number of units consumed.
B) summing the marginal utilities of each unit consumed.
C) multiplying the marginal utility of the last unit consumed by product price.
D) multiplying the marginal utility of the first unit consumed by the number of units consumed.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consumer's demand curve for a product is downsloping because
A) total utility falls below marginal utility as more of a product is consumed.
B) marginal utility diminishes as more of a product is consumed.
C) time becomes less valuable as more of a product is consumed.
D) the income and substitution effects precisely offset each other.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that a consumer purchases a combination of products Y and Z and that the MUy/Py = 30/2 and MUz/Pz = 45/3. To maximize utility, without spending more money, the consumer should
A) purchase less of Y and more of Z.
B) purchase more of Y and less of Z.
C) purchase more of both Y and Z.
D) make no change in the quantities of Y and Z.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prashanth decides to buy a $75 ticket to a particular New York professional hockey game rather than a $50 ticket for a particular Broadway play. We can conclude that Prashanth
A) is relatively unappreciative of the arts.
B) obtains more marginal utility from the play than from the hockey game.
C) has a higher "marginal utility-to-price ratio" for the hockey game than for the play.
D) has recently attended several other Broadway plays.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A child is given $4 of pocket money to be spent on either hard candies or chocolates. Chocolates cost 40 cents and hard candies 80 cents each. The marginal utilities derived from each product are as shown in the following table. 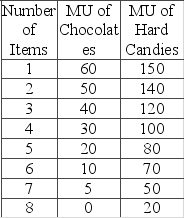 If the child buys either chocolates or hard candies one piece at a time, what will be his first two purchases?
If the child buys either chocolates or hard candies one piece at a time, what will be his first two purchases?
A) a hard candy, followed by another hard candy
B) a hard candy, followed by a chocolate
C) a chocolate, followed by a hard candy
D) a chocolate, followed by another chocolate
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 161 - 180 of 256
Related Exams