A) always outweighs the total welfare costs due to lost surplus.
B) sometimes outweighs the total welfare costs due to lost surplus.
C) never outweighs the total welfare costs due to lost surplus.
D) is a normative argument that has no right answer.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The existence of a monopoly:
A) creates market inefficiencies.
B) causes consumers to get less at a higher price.
C) causes a reduction in total surplus.
D) All of these statements are true.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This graph shows the cost and revenue curves faced by a monopoly. 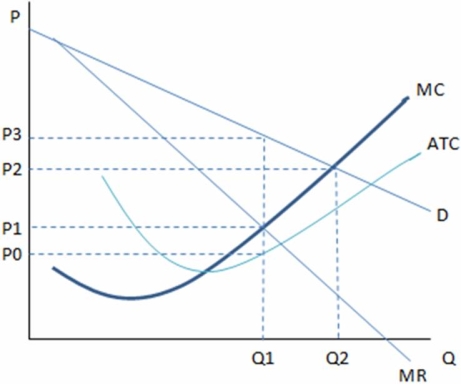 According to the graph,if the perfectly competitive outcome and monopoly outcome are compared,we can see that the:
According to the graph,if the perfectly competitive outcome and monopoly outcome are compared,we can see that the:
A) monopoly creates deadweight loss.
B) perfectly competitive firm would lose money in this industry.
C) perfectly competitive firm would produce Q1 units.
D) monopolist would charge P3 and the perfectly competitive firm would charge P1.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The monopolist's cost curves differ from those of a perfectly competitive firm in that the:
A) marginal cost curve is downward sloping instead of flat.
B) average total cost curve is not necessarily minimized where it crosses marginal cost.
C) average variable cost in no longer equal to marginal cost.
D) The cost curves are the same for a firm regardless of market structure.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
DeBeers was able to profit the most from the diamond market by selling a:
A) lot of diamonds at low prices.
B) few diamonds at high prices.
C) lot of diamonds at high prices.
D) few diamonds at low prices.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The loss of the profit motive by a publicly-owned natural monopoly causes which of the following to happen?
A) Increased pressure from the public to turn a profit
B) Increased pressure from the public to cut costs
C) Decreased incentive to improve efficiency
D) Increased motivation to cut costs
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This graph shows the cost and revenue curves faced by a monopoly. 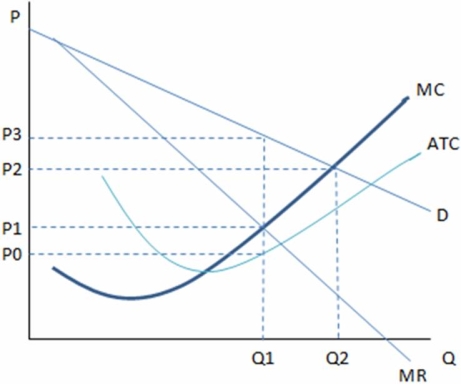 According to the graph shown,if this were a perfectly competitive market,the outcome in the short run would be:
According to the graph shown,if this were a perfectly competitive market,the outcome in the short run would be:
A) Q1, P1.
B) Q1, P3.
C) Q2, P2.
D) The graph is of a monopoly, and therefore there is no way to determine a perfectly competitive outcome.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In practice,placing a price control on a natural monopoly:
A) is easy and commonly practiced.
B) is difficult because of lack of information.
C) always creates the same outcome as public ownership of the industry.
D) is never a good idea.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a government splits a natural monopoly vertically,it is breaking the company up:
A) along its stages of production.
B) into smaller companies providing the same goods.
C) in order to maximize its profits.
D) in order to capture all efficiencies possible.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Natural monopolies:
A) are the only monopolies that are efficient.
B) can capture the lowest production costs possible for the industry.
C) are always protected by government policy.
D) generally earn zero accounting profits due to regulations.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A government-owned monopoly is more likely to:
A) provide a greater quantity of output than a private one.
B) provide output at a lower price than a private one.
C) serve public interest than maximize profit.
D) All of these statements are true.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The regulation of natural monopolies is common in which of the following industries?
A) Electricity
B) Oil
C) Tobacco
D) Alcohol
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The monopolist chooses to produce:
A) where marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
B) at a higher quantity than the perfectly competitive firm.
C) at an efficient outcome.
D) at a cost that is equal to a competitive one.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One barrier to entry into a monopoly market is:
A) the ownership of a key resource or input.
B) too many competitors already in the market.
C) high input costs.
D) few buyers.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With a monopolist's outcome,producer surplus is:
A) higher than that of a competitive market.
B) lower than that of a competitive market.
C) the same as that of a competitive market.
D) Any of these is possible.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some economists argue the best response to a monopoly is to:
A) do whatever the public demands.
B) do nothing at all.
C) never publicly own enterprises because it raises taxes.
D) None of the statements is true.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In theory,placing a price control on a natural monopoly should:
A) have the same outcome as public ownership.
B) create negative economic profits for the company.
C) reduce deadweight loss to zero.
D) be easy for government to figure out because of easily accessible information.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the real world:
A) businesses can easily identify different groups' willingness to pay, so price discrimination is prevalent in every market.
B) price discrimination is practiced less today than it was in the mid-1900s.
C) perfect price discrimination is impossible.
D) price discrimination has only been observed where monopolies are present.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A natural monopolist that sets prices equal to marginal cost will:
A) set a price greater than average total costs.
B) be inefficient.
C) incur losses.
D) earn zero accounting profits.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The monopolist's outcome happens at a:
A) lower price than the perfectly competitive one.
B) higher price than the perfectly competitive one.
C) higher quantity than the perfectly competitive one.
D) equal quantity that is equal to a perfectly competitive one.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 146
Related Exams