A) secondary consumers and top carnivores require less energy than producers.
B) at each step, energy is lost from the system as a result of keeping the organisms alive.
C) as matter passes through ecosystems, some of it is lost to the environment.
D) biomagnification of toxic materials limits the secondary consumers and top carnivores.
E) top carnivores and secondary consumers have a more general diet than primary producers.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the food chain grass → grasshopper → mouse → snake → hawk. How much of the chemical energy fixed by photosynthesis of the grass (100%) is available to the hawk?
A) 0.01%
B) 0.1%
C) 1%
D) 10%
E) 60%
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which trophic level is most vulnerable to extinction?
A) producer level
B) primary consumer level
C) secondary consumer level
D) tertiary consumer level
E) decomposer level
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement best describes what ultimately happens to the chemical energy that is not converted to new biomass in the process of energy transfer between trophic levels in an ecosystem?
A) It is undigested and winds up in the feces and is not passed on to higher trophic levels.
B) It is used by organisms to maintain their life processes through the reactions of cellular respiration.
C) Heat produced by cellular respiration is used by heterotrophs to thermoregulate.
D) It is eliminated as feces or is dissipated into space as heat in accordance with the second law of thermodynamics.
E) It is recycled by decomposers to a form that is once again usable by primary producers.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does phosphorus normally enter ecosystems?
A) cellular respiration
B) photosynthesis
C) rock weathering
D) vulcanism
E) atmospheric phosphorous gas
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following terms encompasses all of the others?
A) heterotrophs
B) herbivores
C) carnivores
D) primary consumers
E) secondary consumers
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In ecosystems, why is the term cycling used to describe material transfer, whereas the term flow is used for energy exchange?
A) Materials are repeatedly used, but energy flows through and out of ecosystems.
B) Both material and energy are recycled and are then transferred to other ecosystems as in a flow.
C) Materials are cycled into ecosystems from other ecosystems, but energy constantly flows within the ecosystem.
D) Both material and energy flow in a never-ending stream within an ecosystem.
E) None of the choices is correct.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement most accurately describes how matter and energy are used in ecosystems?
A) Matter is cycled through ecosystems; energy is not.
B) Energy is cycled through ecosystems; matter is not.
C) Energy can be converted into matter; matter cannot be converted into energy.
D) Matter can be converted into energy; energy cannot be converted into matter.
E) Matter is used in ecosystems; energy is not.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How is it that the open ocean produces the highest net primary productivity of Earth's ecosystems, yet net primary productivity per square metre is relatively low?
A) Oceans contain greater concentrations of nutrients compared to other ecosystems.
B) Oceans receive a lesser amount of solar energy per unit area.
C) Oceans have the largest area of all the ecosystems on Earth.
D) Ocean ecosystems have less species diversity.
E) Oceanic producers are generally much smaller than oceanic consumers.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Photosynthetic organisms are unique to most ecosystems because they
A) synthesize organic compounds they obtain from decaying heterotrophs.
B) synthesize inorganic compounds from organic compounds.
C) use light energy to synthesize organic compounds.
D) use chemical energy to synthesize organic compounds.
E) convert light energy into matter.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The law of conservation of matter states that matter cannot be created, yet matter is sometimes gained or lost to an ecosystem. What is the reason for this seeming contradiction?
A) Chemoautotrophic organisms can convert matter to energy.
B) Matter can be moved in/out of an ecosystem from/to another ecosystem.
C) Photosynthetic organisms convert solar energy to sugars.
D) Detrivores convert matter to energy.
E) Heterotrophs convert heat to energy.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the goal of restoration ecology?
A) to replace a ruined ecosystem with a more suitable ecosystem for that area
B) to speed up the restoration of a degraded ecosystem
C) to completely restore a disturbed ecosystem to its former undisturbed state
D) to prevent further degradation by protecting an area with park status
E) to manage competition between species in human-altered ecosystems
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following lists of organisms is ranked in correct order from lowest to highest percent in production efficiency?
A) mammals, fish, insects
B) insects, fish, mammals
C) fish, insects, mammals
D) insects, mammals, fish
E) mammals, insects, fish
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Hubbard Brook watershed deforestation experiment yielded all of the following results except
A) Most minerals were recycled within a forest ecosystem.
B) The flow of minerals out of a natural watershed was offset by minerals flowing in.
C) Deforestation increased water runoff.
D) The nitrate concentration in waters draining the deforested area became dangerously high.
E) Calcium levels remained high in the soil of deforested areas.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Approximately 1% of the solar radiation that strikes a plant is converted into the chemical bond energy of sugars. Why is this amount so low?
A) Approximately 99% of the solar radiation is converted to heat energy.
B) Only 1% of the wavelengths of visible light are absorbed by photosynthetic pigments.
C) Most solar energy strikes water and land surfaces.
D) Approximately 99% of the solar radiation is reflected.
E) Only the green wavelengths are absorbed by plants for photosynthesis.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The discipline that applies ecological principles to returning degraded ecosystems to a more natural state is known as
A) population viability analysis.
B) landscape ecology.
C) conservation ecology.
D) restoration ecology.
E) resource conservation.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) An ecosystem's trophic structure determines the rate at which energy cycles within the system.
B) At any point in time, it is impossible for consumers to outnumber producers in an ecosystem.
C) Chemoautotrophic prokaryotes near deep-sea vents are primary producers.
D) There has been a well-documented increase in atmospheric nitrogen over the past several decades.
E) The reservoir of ecosystem phosphorous is the atmosphere.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following food web to answer the questions below.
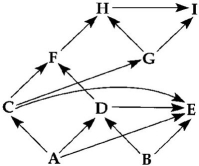 Diagram of a food web (arrows represent energy flow and letters represent species)
-If the figure above represents a marine food web, the smallest organism might be
Diagram of a food web (arrows represent energy flow and letters represent species)
-If the figure above represents a marine food web, the smallest organism might be
A) A.
B) F.
C) C.
D) I.
E) E.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How do the Taylor Glacier bacteria produce their energy?
A) photosynthesis
B) heterotrophism
C) chemoautotrophism
D) thermophobism
E) chemosynthesis
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In terms of nutrient cycling, why does timber harvesting in a temperate forest cause less ecological devastation than timber harvesting in tropical rain forests?
A) Trees are generally less numerous in temperate forests, so fewer nutrients will be removed from the temperate forest ecosystem during a harvest.
B) Temperate forest tree species require fewer nutrients to survive than their tropical counterpart species, so a harvest removes fewer nutrients from the temperate ecosystem.
C) The warmer temperatures in the tropics influence rain forest species to assimilate nutrients more slowly, so tropical nutrient absorption is much slower than in temperate forests.
D) There are far fewer decomposers in tropical rain forests, so turning organic matter into usable nutrients is a slower process than in temperate forest ecosystems.
E) Typical harvests remove up to 75% of the nutrients in the woody trunks of tropical rain forest trees, leaving nutrient-impoverished soils behind.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 89
Related Exams