A) The concentration of the reactants equals the concentration of the products.
B) The rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
C) All of the reactants have been converted to the products of the reaction.
D) All of the products have been converted to the reactants of the reaction.
E) Both the forward and the reverse reactions have stopped with no net effect on the concentration of the reactants and the products.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In comparing covalent bonds and ionic bonds, which of the following would you expect?
A) An atom can form covalent bonds with multiple partner atoms, but only a single ionic bond with a single partner atom.
B) Covalent bonds and ionic bonds occupy opposite ends of a continuous spectrum, from nearly equal to completely unequal sharing of electrons.
C) Both involve electrical attraction between the electrons of one atom and the nucleus of the other atom.
D) Ionic interactions remain when covalent bonds are broken in water. Ionic bonds are much stronger than covalent bonds.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Van der Waals interactions result when
A) hybrid orbitals overlap.
B) electrons are not symmetrically distributed in a molecule.
C) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water.
D) two polar covalent bonds react.
E) a hydrogen atom loses an electron.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. You are investigating how chemical reactions occur. You place two reactants together and measure the concentration of product at regular intervals. After a time, the amount of product becomes stable. -The reactivity of an atom arises from
A) the average distance of the outermost electron shell from the nucleus.
B) the existence of unpaired electrons in the valence shell.
C) the sum of the potential energies of all the electron shells.
D) the potential energy of the valence shell.
E) the energy difference between the s and p orbitals.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Phosphorus-32, a radioactive isotope of phosphorus-31 (atomic number 15) , undergoes a form of radioactive decay whereby a neutron turns into a proton and emits radiation in the form of an electron. What is the product of such radioactive decay of phosphorus-32?
A) phosphorus-31
B) a positively charged phosphorus-31 ion
C) a negatively charged phosphorus-32 ion
D) sulphur-32 (atomic number 16)
E) the conversion of the phosphorus-32 atom into pure energy
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a salamander relied on hydrogen bonds to cling to surfaces, what type of surface would cause the most problems for this animal?
A) a surface coated with a thin film of water
B) a surface made with carbon and hydrogen atoms covalently bonded together
C) a surface made with carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms covalently bonded together
D) a surface made with carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms covalently bonded together
E) a surface made with silicon and oxygen atoms covalently bonded together
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these systems is least likely to be at chemical equilibrium?
A) a test tube of living cells
B) a test tube of organic molecules, kept in the freezer
C) a test tube of dry organic molecules, kept at room temperature
D) a test tube of organic molecules dissolved in water, kept at room temperature
E) a test tube of dead cells in water, kept at room temperature
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chemical bond/interaction strength appears in what order?
A) Hydrogen > covalent > ionic > VanderWaals.
B) Covalent > ionic > hydrogen > VanderWaals.
C) Covalent > hydrogen > ionic > VanderWaals.
D) VanderWaals > hydrogen > ionic > covalent.
E) Ionic > hydrogen > VanderWaals > covalent.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes the relationship between the atoms described below?


A) They are isomers.
B) They are polymers.
C) They are isotopes.
D) They contain 1 and 3 protons, respectively.
E) They each contain 1 neutron.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A dalton is a unit of
A) distance.
B) weight.
C) mass.
D) bond strength.
E) energy.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
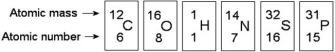 -How many electrons does an atom of sulphur have in its valence shell (see the figure above) ?
-How many electrons does an atom of sulphur have in its valence shell (see the figure above) ?
A) 4
B) 6
C) 8
D) 16
E) 32
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The combining of the metal, sodium, with the poisonous gas, chlorine, to produce an edible product, salt, is a good example of
A) essential elements.
B) emergent properties.
C) covalent interactions.
D) Van der Waals interactions.
E) chemical equilibrium.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following molecules contains the most polar covalent bond?
A) H₂
B) O₂
C) CO₂
D) H₂O
E) CH₄
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living matter?
A) carbon, sodium, hydrogen, nitrogen
B) carbon, oxygen, phosphorus, hydrogen
C) oxygen, hydrogen, calcium, nitrogen
D) carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen
E) carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, calcium
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. You are investigating how chemical reactions occur. You place two reactants together and measure the concentration of product at regular intervals. After a time, the amount of product becomes stable. -Compared with ³¹P, the radioactive isotope ³²P has
A) a different atomic number.
B) a different charge.
C) one more proton.
D) one more electron.
E) one more neutron.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. You are investigating how chemical reactions occur. You place two reactants together and measure the concentration of product at regular intervals. After a time, the amount of product becomes stable. -This solution has
A) used up all the reactants, so no more product can be made.
B) used up all the product, so no more reaction is occurring.
C) reached equilibrium, where there is no more formation of the product.
D) reached equilibrium, where the net formation of both product and reactants is neutral.
E) become saturated.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following pairs of atoms would be most likely to form a polar covalent bond?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Atoms whose outer electron shells contain 8 electrons tend to
A) form ions in aqueous solutions.
B) form hydrogen bonds in aqueous solutions.
C) be stable and chemically nonreactive, or inert.
D) be gaseous at room temperature.
E) be both chemically inert and gaseous at room temperature.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Plants that are capable of thriving in serpentine soil can do so as a result of
A) natural selection.
B) chance.
C) chemical neutralization of contaminants.
D) generating their own essential elements.
E) serpentine soil poses no challenge to plants.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The atomic number of each atom is given to the left of each of the elements below. Which of the atoms has the same valence as carbon ( 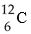 ) ?
) ?
A) ₇N nitrogen
B) ₉F fluorine
C) ₁₀Ne neon
D) ₁₂Mg magnesium
E) ₁₄Si silicon
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 90
Related Exams