A) In Batesian mimicry the model must behave differently than the mimic; in Müllerian mimicry they behave the same.
B) In Batesian mimicry the model must be more dangerous than the mimic; in Müllerian mimicry they are both dangerous.
C) Batesian mimicry does not differ from Müllerian mimicry. Two different scientists discovered these two types at the same time, and they disagreed on what to call it.
D) Batesian mimicry differs from Müllerian mimicry in that they occur on different continents-Batesian on the North American and Müllerian on the European.
E) Batesian mimicry involves invertebrates; Müllerian mimicry involves vertebrates.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the fundamental and realized niche are true? Check all that apply.
A) A species' realized niche could be the same size as its fundamental niche.
B) A species' realized niche could be smaller than its fundamental niche.
C) A species' fundamental niche can be smaller than its realized niche.
D) The extent of the realized niche is determined, in part, by interspecific competition.
E) The extent of the fundamental niche is determined, in part, by conditions of the physical environment.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement is the correct interpretation of the graph? 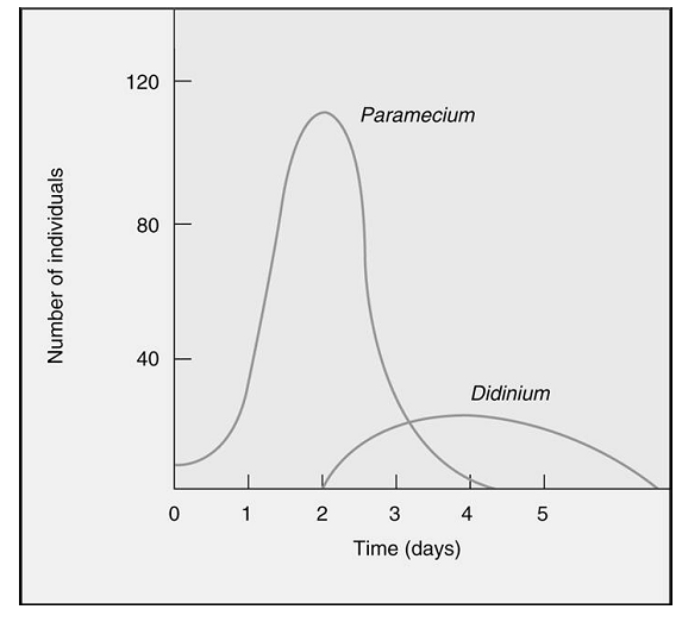
A) The population of Didinium goes extinct with the addition of Paramecium on day 4.
B) The population of Didinium continues to increase and remains high even after the extinction of the Paramecium.
C) The population of Paramecium goes extinct with the addition of Didinium on day 8.
D) The population of Didinium increased but then went extinct after the population of Paramecium went extinct.
E) The population of Didinium is able to increase at the expense of the Paramecium population. After a brief period both populations are able to coexist.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a producer?
A) gymnosperm
B) cricket
C) garden spider
D) blue jay
E) red-tailed hawk
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are types of symbioses? Check all that apply.
A) Batesian mimicry
B) commensalism
C) predation
D) parasitism
E) mutualism
F) Müllerian mimicry
H) D) and F)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You have been studying the relationship between jackals and tigers in India. Until recently, the only relationship you have observed is that jackals will attach themselves to a particular tiger and follow it at a safe distance in order to feed on the big cat's kills. However, recently you observed a jackal alerting a tiger to a kill with a loud cry. If you continue to observe this alerting behavior, you might change the categorization of the jackal/tiger relationship from ___________ to __________________.
A) mutualism; parasitism
B) mutualism; commensalism
C) commensalism; mutualism
D) parasitism; mutualism
E) competition; predation
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following figure shows studies in a stream where enclosures were set up either with trout or with no trout. Which statement is a correct interpretation of the graph about trout, invertebrates, and algae? 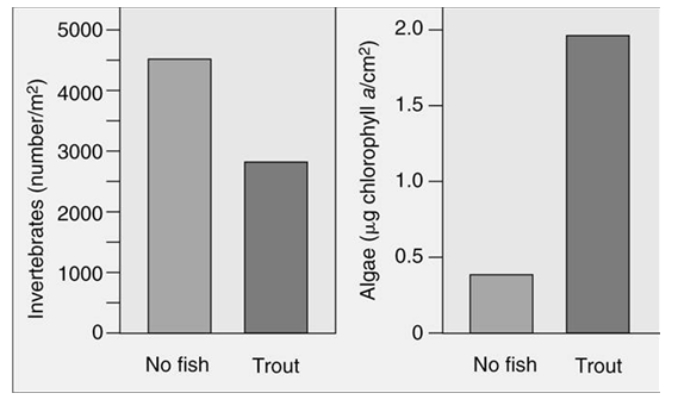
A) If trout are present in a system, algae production is low and invertebrate population levels are also low.
B) If trout are present in a system, algae production is high and invertebrate population levels are also high.
C) If trout are present in a system, algae production is high and invertebrate population levels are low.
D) Trout do not seem to affect the algae production; only the invertebrate populations are affected.
E) Trout do affect the algae production but not the invertebrate populations.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following observations were an outcome of studies by David Tilman and coworkers at Cedar Creek, Minnesota on ecosystem stability? Check all that apply.
A) Plots with more species showed less year-to-year variation in biomass.
B) Species-rich plots were less affected by drought than species-poor plots.
C) Over-yielding was observed in more recent work at Cedar Creek.
D) Nitrogen uptake and total biomass produced were negatively correlated to species richness.
E) More diverse plots were less susceptible to invasion by new species.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
A, B, C, E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What structures evolved in the Acacia in order to develop a mutualistic relationship with the Pseudomyrmex ant?
A) nectaries and Beltian bodies
B) nectaries and tough fibrous leaves
C) hollow thorns and a fibrous root system
D) secondary compounds and Beltian bodies
E) secondary compounds and tough fibrous leaves
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about an ecosystem receiving a moderate level of continued disturbance are true? Check all that apply.
A) A moderate level of continued disturbance predicts that most communities eventually reach an end-state or climax community.
B) A moderate level of continued disturbance should lead to increases in species richness.
C) A moderate level of continued disturbance tends to lead to the dominance of K-selected species.
D) An example of a moderate level of continued disturbance would be a tree fall in a mature rain forest.
E) A moderate level of continued disturbance should lead to all successional stages being present in the community at the same time.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement correctly interprets the graph? 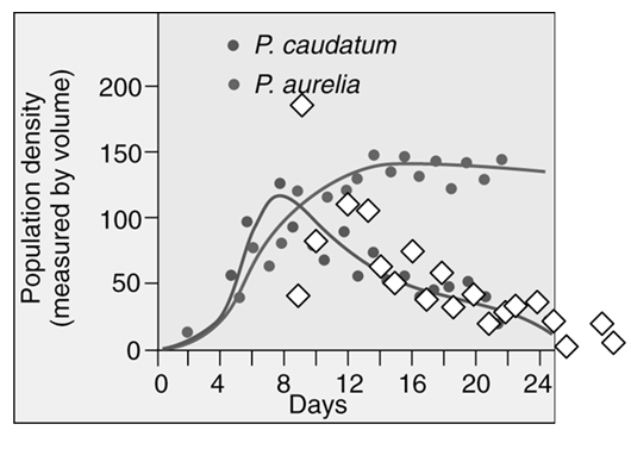
A) Paramecium caudatum drives Paramecium aurelia to near extinction.
B) Paramecium aurelia drives Paramecium caudatum to near extinction.
C) Paramecium caudatum and Paramecium aurelia are able to compete for the same resource and their population densities are not affected.
D) Paramecium caudatum and Paramecium aurelia are unable to exist and both populations go extinct after 24 days.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Phosphorus deficiency often appears early in plant growth and results in stunting. Which of the following are reasons why a deficiency in phosphorus would cause growth abnormalities in plants?
A) Phosphorus is required for the storage and transfer of energy.
B) Phosphorus is required for the production of amino acids and the synthesis of proteins.
C) Phosphorus is required for DNA replication.
D) Phosphorus is necessary for building cellular structures responsible for regulating the flow of compounds into and out of a cell.
E) Without phosphorus, cellular division is impeded.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In studies of two species of barnacles in the marine intertidal zone it was observed that Chthamalus can live in the upper intertidal zone and the lower intertidal zone if Semibalanus is absent, and Semibalanus can only live in the lower zone because it is more subject to dehydration. Based on this, which of the following statements are true? Check all that apply.
A) The realized niches of the two species differ.
B) The fundamental niche of Chthamalus is larger than its realized niche.
C) The fundamental niche of Chthamalus is larger than the fundamental niche of Semibalanus.
D) The fundamental and the realized niches of Chthamalus are the same.
E) The fundamental and the realized niches of Semibalanus are the same.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 13 of 13
Related Exams