A) begin interpretation of the function by examining the discriminant coefficients
B) check the statistical significance of the function
C) standardize the discriminant coefficients
D) classify individuals using the discriminant function
E) none of the above
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions focus on Multidimensional Scaling: -Kruskal's stress
A) is an index of variation.
B) is a measure of central tendency.
C) is a lack of fit index.
D) is an index of reproducibility.
E) is an index of dispersion.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions focus on Multidimensional Scaling: -Which of the following are not methods for naming underlying dimensions in multidimensional scaling?
A) After subjects have evaluated objects in terms of defined attributes, the researcher can correlate the attribute scale scores for each object with the coordinates for each object in the perceptual map.
B) Managers may use their experience to interpret the dimensions.
C) Researchers may attempt to relate the dimensions to actual attributes of the objects under study.
D) Researchers may name the resulting dimensions based on a priori hypotheses.
E) All of the above are methods for naming dimensions in MDS.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
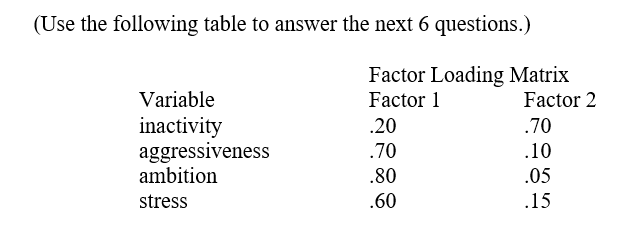 -What proportion of the variability in the data is accounted for by the two factor solution?
-What proportion of the variability in the data is accounted for by the two factor solution?
A) 51%
B) 100%
C) 78%
D) 27%
E) more information is needed
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Use the information below to answer the next three questions.) In a five variable two group discriminant analysis, the following weights were derived: V1 = .561, V2 = .030, V3 = .049, V4 = .701, V5 = -.021. The corresponding pooled standard deviations are S1 = 4.60, S2 = 1.23, S3 = 10.40, S4 = 13.23, and S5 = 8.30. For individual 1, the values for the four variables were X1 = 10, X2 = 3, X3 = 25, X4 = 36, and X5 = 42. -Individual 1's standardized discriminant score is
A) 363.08.
B) 365.21.
C) 372.53.
D) 380.47.
E) 392.03.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To determine the "hit rate" in a matrix of actual vs. predicted classifications, the analyst should focus most of his/her attention on the
A) individual column totals.
B) individual row totals.
C) both the individual column and row totals.
D) total number of subjects in the diagonal of the matrix.
E) average of the column totals.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rotation of the original factor analysis solution typically results in
A) an improved substantive interpretation of the solution.
B) a change in the achieved communality estimate for any one variable.
C) a change in the proportion of variance accounted for by any one factor.
D) a and b above.
E) a and c above.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When making a decision as to how many factors to retain in the final factor analysis solution, the researcher should
A) examine the size of the latent roots.
B) plot the size of the latent roots against the number of factors.
C) examine the amount of covariability recovery.
D) examine the amount of variability recovery.
E) all of the above.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -For which pair of variables is the estimated original correlation the highest?
-For which pair of variables is the estimated original correlation the highest?
A) inactivity and aggressiveness
B) inactivity and ambition
C) aggressiveness and stress
D) aggressiveness and ambition
E) stress and ambition
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding cluster analysis?
A) Different methods of cluster analysis can produce different results.
B) There is consensus on which method of cluster analysis is best under all circumstances.
C) Nodal methods of factor analysis involve the selection of an object or objects to serve as focal points for the clusters.
D) The average linkage method works better than the other hierarchical method of cluster analysis.
E) Cluster analysis seeks to identify natural groupings of objects given the multivariate nature of the data.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a key decision that needs to be made when factor analyzing data?
A) What is the dependent variable?
B) Should factor analysis be applied to the data?
C) Which factor model should be used?
D) Should the initial solution be rotated?
E) All of the above are key decisions that need to be made when factor analyzing data.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT one of the quantities used to assess the relative importance of variables in discriminating between groups in discriminant analysis?
A) the mean differences of the groups on each variable
B) the discriminant coefficients
C) the pairwise correlations between the variable and the discriminant score
D) the standardized coefficients
E) Both b and c are not quantities used to assess the relative importance of variables in discriminating between groups.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Use the information below to answer the next three questions.) In a five variable two group discriminant analysis, the following weights were derived: V1 = .561, V2 = .030, V3 = .049, V4 = .701, V5 = -.021. The corresponding pooled standard deviations are S1 = 4.60, S2 = 1.23, S3 = 10.40, S4 = 13.23, and S5 = 8.30. For individual 1, the values for the four variables were X1 = 10, X2 = 3, X3 = 25, X4 = 36, and X5 = 42. -Which variable is least important in discriminating between the two groups?
A) X1
B) X2
C) X3
D) X4
E) X5
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A factor loading is typically assumed to be significant if its value is in the neighborhood of
A) .20 to .25.
B) .25 to .30.
C) .30 to .35.
D) .35 to .40.
E) .40 to .45.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The square of a factor loading indicates
A) the proportion of variation accounted for by the factor.
B) the proportion of variation in the variable accounted for by the complete set of possible factors.
C) the proportion of variation shared by one pair of variables.
D) the proportion of variation in the variable shared by all variables in the analysis.
E) none of the above.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To test whether the cluster results offer a reasonable summary of the similarity, correlation, or distance matrix, that is, are the individual clusters sufficiently homogeneous and is the system as a whole consistent with the input similarities, the following procedure(s) can be performed:
A) the variables used to determine the clusters can be tested to determine if the clusters have statistically different values across the groups.
B) the reliability of the estimates can be assessed by splitting the data into multiple subsets and assessing whether the same clusters are produced when the subsets are analyzed.
C) significance tests can be performed that compare the clusters on variables not used to generate the solution.
D) All of the above procedures are correct.
E) Both b and c are correct.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cutting score in a discriminant analysis is the score that
A) divides the mean discriminant scores.
B) determines which discriminant functions are statistically significant.
C) determines which discriminant coefficients are statistically significant.
D) is used as a guide to classify subjects.
E) is a and d above.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
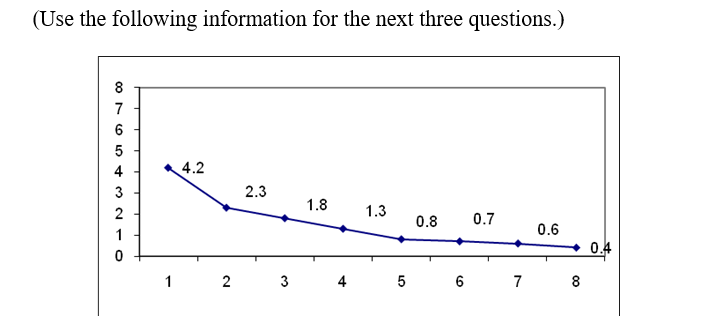 -Use the traditional eigenvalue test to determine the number of factors that should be retained in the factor analysis. How many factors should be retained?
-Use the traditional eigenvalue test to determine the number of factors that should be retained in the factor analysis. How many factors should be retained?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Principal components factor analysis seeks to
A) transform a set of interrelated variables into a set of unrelated linear combinations of these variables.
B) choose the set of linear combinations so that each factor accounts for an increasing proportion of the variance in the original variables.
C) choose the set of linear combinations so that the factors are uncorrelated with each other.
D) a and b.
E) a and c.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Varimax rotation of a factor solution attempts to
A) maintain the right angles between the factors.
B) enhance the substantive interpretation of the unrotated factor solution.
C) force the entries in the columns of the factor loading matrix to be near 0 or 1.
D) all of the above.
E) a and b above.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 86
Related Exams