A) line (a) .
B) line (b) .
C) line (c) because taxes and transfers have no effect on income distribution.
D) line (d) .
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
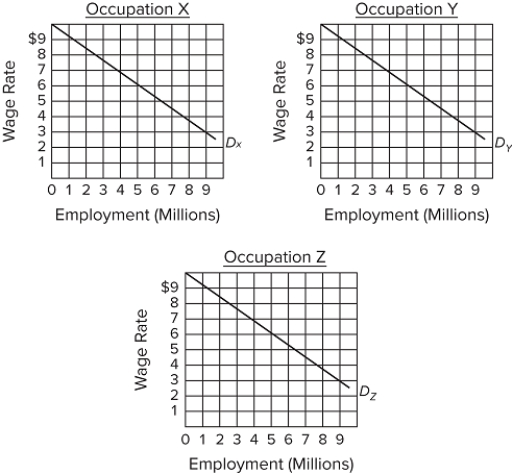 Assumptions: (1) the labor force comprises 9 million men and 9 million women workers; (2) the economy has 3 occupations, X, Y, and Z, each having identical demand curves for labor; (3) male and female workers are homogeneous with respect to their labor-market capabilities; (4) women are discriminated against by being excluded from occupations X and Y and are confined to Z; and (5) aside from discrimination, the economy is competitive, and workers seek to maximize their earnings.Refer to the diagram and list of assumptions. If discrimination is ended,
Assumptions: (1) the labor force comprises 9 million men and 9 million women workers; (2) the economy has 3 occupations, X, Y, and Z, each having identical demand curves for labor; (3) male and female workers are homogeneous with respect to their labor-market capabilities; (4) women are discriminated against by being excluded from occupations X and Y and are confined to Z; and (5) aside from discrimination, the economy is competitive, and workers seek to maximize their earnings.Refer to the diagram and list of assumptions. If discrimination is ended,
A) men will leave occupations X and Y and enter occupation Z.
B) 4 million women will leave occupation Z, with 2 million entering occupation X and 2 million entering occupation Y.
C) 3 million women will leave occupation Z, with 1.5 million entering occupation X and 1.5 million entering occupation Y.
D) 3 million women will leave occupation Z, all of whom will enter industry X.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would be considered part of income?
A) wages and salaries
B) the value of a house
C) corporate stock holdings
D) money in a bank account
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The distribution of wealth in the United States is such that it
A) is randomly distributed among income classes.
B) has no perceptible impact on the distribution of income.
C) reduces income inequality.
D) contributes to income inequality.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Each of the following contributes to income inequality except
A) differences in ability and training.
B) differences in job tastes.
C) differences in wealth ownership.
D) government transfers.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A particular woman is denied on-the-job training because women on average are more likely to drop out of the workforce than men. This illustrates
A) occupational segregation.
B) the crowding model.
C) the taste-for-discrimination model.
D) statistical discrimination.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the taste-for-discrimination model,
A) discriminatory employers behave as if employing nonpreferred-race workers adds to costs.
B) individual workers are judged by the characteristics of the groups to which they belong.
C) prejudiced white employers will never hire African-American workers.
D) women and minorities are confined to a limited number of occupations.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a major reason for the growing income inequality in the United States since 1980?
A) higher marginal tax rates
B) unemployment benefits
C) rising number of skilled workers
D) import competition
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference between income and wealth is that income
A) is accumulated, while wealth is earned.
B) refers to a flow of earnings, while wealth is the stock of assets one has.
C) is measured at a point in time, while wealth is measured over a period of time.
D) may not be in cash, while wealth is in cash.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Since the implementation of TANF in 1996, the U.S. welfare rolls have fallen by roughly one-half and participation remains low in 2017.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
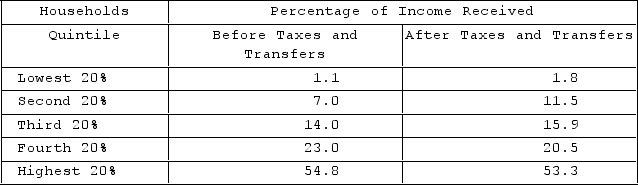 Refer to the table. The decline in percentage of income received from before taxes and transfers to after taxes and transfers is greatest for the
Refer to the table. The decline in percentage of income received from before taxes and transfers to after taxes and transfers is greatest for the
A) third 20 percent of households.
B) second 20 percent of households.
C) highest 20 percent of households.
D) fourth 20 percent of households.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The top 20 percent of U.S. income earners receive nearly 80 percent of total U.S. income.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
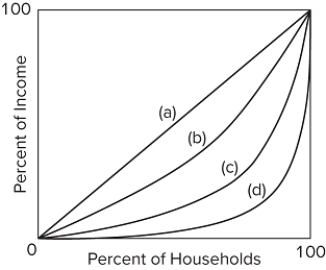 Refer to the figure. A nation that has an income distribution of perfect equality would be represented by curve
Refer to the figure. A nation that has an income distribution of perfect equality would be represented by curve
A) a.
B) b.
C) c.
D) d.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cause of the unequal distribution of income in the United States is
A) differences in work preferences and risks.
B) differences in noncash transfers.
C) high expenditures for social insurance.
D) a low benefit-reduction rate for income.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If there is a widespread bias against African-American workers, an increase in the collective discrimination coefficients of employers will
A) reduce the African-American wage rate, increase African-American employment, and lower the actual African-American-white wage ratio.
B) reduce the African-American wage rate, decrease African-American employment, and lower the actual African-American-white wage ratio.
C) increase the African-American wage rate, increase African-American employment, and increase the actual African-American-white wage ratio.
D) increase the African-American wage rate, reduce African-American employment, and increase the actual African-American-white wage ratio.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Medicaid
A) helps finance medical expenses for those participating in the TANF and Supplemental Security Income programs.
B) has been abandoned in favor of privately provided medical insurance.
C) is a program of medical insurance for the aged and retired.
D) is a compulsory national health insurance program that only covers preventative medical services.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The crowding model of discrimination suggests that
A) women and selected minorities are systematically excluded from high-paying occupations and crowded into low-paying occupations, decreasing their wages and reducing domestic output.
B) employers having high discrimination coefficients will be crowded out by nondiscriminating employers in the long run.
C) firms will base hiring decisions on group averages, rather than on individual characteristics and productivity.
D) occupational segregation is largely the result of freely made rational choices of women and minorities.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An employer is prejudiced, prefers to hire white rather than Hispanic workers, and is willing to pay higher wages to obtain white workers. This illustrates
A) reverse discrimination.
B) the crowding model.
C) the taste-for-discrimination model.
D) statistical discrimination.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a prejudiced white employer behaves as if there is a disutility from hiring an African-American worker, then this disutility is measured by the
A) employment coefficient.
B) discrimination coefficient.
C) occupational coefficient.
D) affirmative action coefficient.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The equality-efficiency trade-off would be most closely associated with which one of the following statements?
A) The rich get richer and the poor get poorer.
B) The only way to create income equality is to take from the rich and give to the poor.
C) If cutting the income pie in more equal slices tends to shrink the pie, what amount of shrinkage will society tolerate?
D) People are less concerned with the larger question of income distribution than they are with the more specific issue of income inadequacy.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 201 - 220 of 324
Related Exams