A) in a recession.
B) not in long-run equilibrium.
C) producing a quantity less than the long-run aggregate supply.
D) All of these are true.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the government increases spending by $400 billion, and the MPC is 0.75, the change in GDP will be:
A) $400 billion.
B) $1,600 billion.
C) $300 billion.
D) $1,200 billion.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following events would cause a demand shock?
A) Refinery capacity in the United States drops permanently.
B) A new pest destroys much of the alfalfa crop in a given year.
C) The government spends less on infrastructure maintenance.
D) Housing prices fall.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure shown displays various economic outcomes. 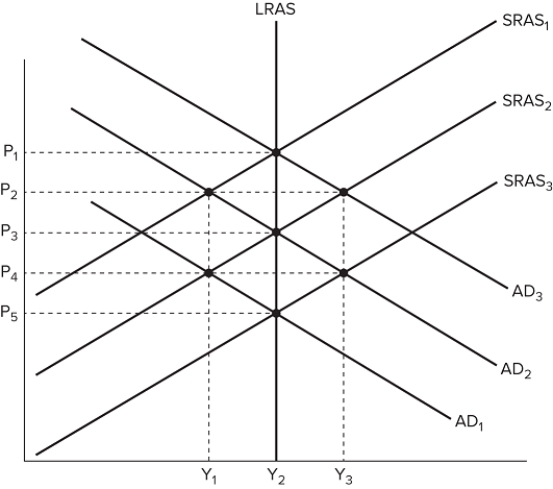 If the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD2 to AD1, the resulting price and output in the short run would be:
If the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD2 to AD1, the resulting price and output in the short run would be:
A) P 1 and Y 1.
B) P 3 and Y 1.
C) P 4 and Y 1.
D) P 4 and Y 2.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the 1970s, the U.S. economy experienced high rates of inflation and limited economic growth. This phenomenon is often called:
A) stagflation.
B) inflagnation.
C) contractionary policy.
D) economic malaise.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What occurs when the price level increases?
A) People demand a smaller aggregate quantity of goods and services.
B) Consumers feel wealthier.
C) The same real value of assets is held by the public, regardless of the change in the price level.
D) People want to spend more.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The aggregate supply and aggregate demand model describes the:
A) overall health of the economy.
B) overall effect of large markets within the economy.
C) way sellers and buyers interact within a particular market.
D) way unemployment affects output, ignoring the impact of the price level.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The long-run aggregate supply curve:
A) is affected by the price level.
B) never moves.
C) shifts to the right when the economy experiences economic growth.
D) shifts to the left when the economy experiences economic growth.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The aggregate supply curve shows:
A) the relationship between the overall price level and firms' total production.
B) the relationship between the overall price level and firms' investment decisions.
C) the total production of all firms in an economy at every given demand level.
D) the total production of all firms in an economy for every level of profit.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a cost of production?
A) Fuel
B) Labor
C) Advertising
D) Rent
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Increases in the overall price level:
A) increase people's dollar-denominated wealth.
B) generally have no effect on spending.
C) increase consumption.
D) reduce consumption.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If U.S. prices increase relative to the rest of the world, we would expect imports to _______ and exports to _______.
A) increase; decrease
B) decrease; increase
C) increase; increase
D) decrease; decrease
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The government might increase spending to end a recession because:
A) allowing short-run aggregate supply to adjust back to the long run can take a long time.
B) it causes prices to be lower in the new long-run equilibrium.
C) the economy enjoys a higher level of output in the long run.
D) None of these explain why the government might increase its spending to end a recession.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During a recession, analysts at the CBO project that the economy is operating $1.5 trillion below potential output. Assuming the MPC is 0.8, by how much would the government have to increase spending to restore potential output?
A) $500 billion
B) $300 billion
C) $1.2 trillion
D) $800 billion
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A temporary decrease in the price of oil is a:
A) short-run supply shock.
B) long-run supply shock.
C) demand shock.
D) The changing price of oil would not influence aggregate demand or supply.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When are firms willing to change the aggregate quantity of output supplied based on price?
A) In the short run only
B) In the long run only
C) In the short and long run
D) Price never affects the quantity that firms supply.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an economy is in a recession, the government might _______ spending to _______ aggregate demand.
A) increase; increase
B) decrease; decrease
C) increase; decrease
D) decrease; increase
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a component of aggregate demand?
A) Consumption
B) Investment
C) Net exports
D) All of these are components of aggregate demand.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an economy is in a recession, it means that:
A) the economy is not in long-run equilibrium.
B) total output is less than potential output.
C) the short-run equilibrium lies to the left of the long-run aggregate supply curve.
D) All of these are true.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The negative relationship that exists between the price level and aggregate expenditure partially explains why the aggregate demand curve is:
A) downward sloping.
B) upward sloping.
C) perfectly elastic.
D) perfectly inelastic.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 166
Related Exams