B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The zones found in an epiphyseal plate are A: Calcified cartilage B: Hypertrophic cartilage C: Ossification D: Resting cartilage E: Proliferating cartilage The correct order for these zones, beginning with the edge closest to the epiphysis and proceeding toward the diaphysis, is
A) c - a - b - e - d
B) d - b - e - a - c
C) e - d - a - c - b
D) c - d - e - a - b
E) d - e - b - a - c
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bone is considered an important storage reservoir for
A) calcium, phosphate, and lipids.
B) steroids, proteins, and complex carbohydrates.
C) glycogen, nitrogenous bases, and calcium.
D) phosphate, glycogen, and nonpolar amino acids.
E) calcium, complex carbohydrates, and polar amino acids.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During appositional growth of cartilage, the cells that produce the matrix are the
A) chondrocytes.
B) osteocytes.
C) fibroblasts.
D) chondroblasts.
E) osteoblasts.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a bone is immersed in a weak acid such as vinegar for several days, its inorganic components will dissolve. What will be the result of such an experiment?
A) The bone will dissolve completely.
B) The compact bone will dissolve, leaving only the inner spongy bone.
C) The bone will become extremely brittle.
D) The bone will become soft and bendable.
E) The spongy bone will dissolve, leaving only the outer compact bone.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Mature cartilage is avascular.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Once we reach adulthood and our bones are fully formed and hardened, they cannot be remodeled.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is an accurate description of appositional bone growth?
A) Osteoblasts build bone at the circumferential lamellae while osteoclasts widen the medullary cavity.
B) Osteoclasts build bone at the concentric lamellae while osteoblasts build bone at the interstitial lamellae.
C) Osteoblasts build bone at the concentric lamellae while osteoclasts build bone at the epiphyses.
D) Osteocytes build bone at the interstitial lamellae while osteoclasts expand the length of the medullary cavity.
E) Osteocytes and osteoclasts expand the bone at its epiphyses; chondrocytes construct cartilage.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Spongy bone
A) contains no osteocytes.
B) has spaces filled with yellow marrow.
C) is composed of tubular units called osteons.
D) forms diploe in the cranial bones.
E) All of the choices are correct.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An osteoclast has a ruffled border and multiple nuclei.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is a change in bone architecture or mass related to aging?
A) Insufficient calcification
B) Demineralization
C) Reduction in the organic content of the matrix
D) Loss of flexibility and increase in brittleness
E) All of the choices are correct.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mechanical stress of bones, such as that caused by weight lifting, is detected by
A) osteocytes, which then communicate to osteoblasts to increase synthesis of osteoid.
B) osteoclasts, which then communicate to osteocytes to increase the size of lacunae.
C) chondrocytes, which then trigger osteoblasts to increase bone in a lengthwise fashion.
D) osteoblasts, which then communicate to osteocytes and osteoclasts to deposit more hydroxyapatite.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In adults, an area of compact bone called the epiphyseal tract replaces the epiphyseal plate.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What gives bone its flexibility?
A) Inorganic salts
B) Yellow bone marrow
C) Collagen fibers
D) Trabeculae
E) Elastic fibers
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
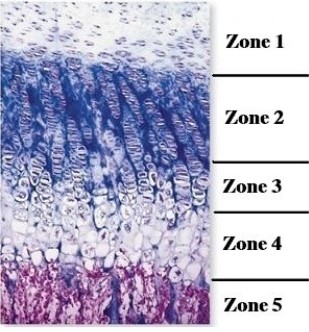 -This figure illustrates epiphyseal plate morphology. Which is the zone of proliferating cartilage?
-This figure illustrates epiphyseal plate morphology. Which is the zone of proliferating cartilage?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The flat bones of the cranium form by intramembranous ossification.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
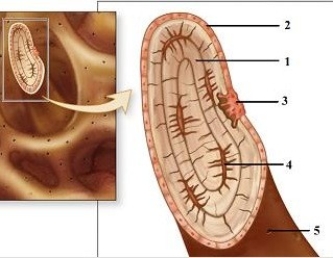 -This figure illustrates the microscopic anatomy of spongy bone. Which is a mature bone cell?
-This figure illustrates the microscopic anatomy of spongy bone. Which is a mature bone cell?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) None of the choices is correct.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The periosteum is anchored to the bone by collagen fibers called ________ fibers.
A) transverse
B) perforating
C) penetrating
D) connecting
E) cementing
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -This figure illustrates the microscopic anatomy of spongy bone. Which number indicates a central canal?
-This figure illustrates the microscopic anatomy of spongy bone. Which number indicates a central canal?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 5
E) None of the choices is correct.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which bone forms by intramembranous ossification?
A) Zygomatic
B) Radius
C) Axis
D) Hamate
E) First metatarsal
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 119
Related Exams