A) the size of the order.
B) the frequency of the order.
C) when orders are placed during the year.
D) the length of the relationship with the manufacturer.
E) the marketing activities they are expected to perform in the future.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Instead of everyday low prices (EDLP) , supermarkets prefer a(n) ________ approach, which is based on frequent specials where prices are temporarily lowered for a brief period of time and then raised again.
A) a fixed-price
B) an alternative pricing
C) a Hi-Lo pricing
D) a bundle-pricing
E) a dynamic pricing policy
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these is a profit-oriented approach to pricing?
A) skimming pricing
B) target pricing
C) loss-leader pricing
D) target return-on-investment pricing
E) standard markup pricing
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A fixed-price policy refers to
A) setting different prices for products and services in real time in response to supply and demand conditions.
B) setting the price of an entire line of products at a single specific pricing point.
C) simultaneously setting prices for all items in a product line to cover the total cost and produce a profit for the complete line, not necessarily for each item.
D) adding a fixed percentage to the cost of all items in a specific product class.
E) setting one price for all buyers of a product or service.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A promotional allowance is
A) a onetime discount to promote the product that must be used within a certain time frame.
B) the cash payments or an extra amount of "free goods" awarded sellers in the marketing channel for undertaking certain advertising or selling activities to promote the product.
C) the return of money to promote the product based on proof of purchase.
D) a short-term price reduction when consumer demand takes a significant and unexpected dip.
E) an incentive, such as trips, cruises, jewelry, etc., presented to brand-loyal customers.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A new car dealer can reduce the price you pay without cutting the list price of a new Ford F-150 pickup truck by offering you a ________ of $1,000 for your 2009 Nissan Altima.
A) cash discount
B) functional discount
C) seasonal discount
D) trade-in allowance
E) promotional allowance
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these is a cost-oriented approach to pricing?
A) cost-plus pricing
B) skimming pricing
C) prestige pricing
D) loss-leader pricing
E) bundle pricing
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these statements regarding odd-even pricing is most accurate?
A) Odd-even pricing is designed to give the consumer a better set of pricing alternatives.
B) Odd-even pricing can be used in conjunction with a skimming pricing strategy, but should not be used with a penetration pricing strategy.
C) Odd-even pricing does not work if the product is health care-related.
D) Overuse of odd-ending prices tends to mute its effect on demand.
E) Odd-ending prices are best used with large ticket items; it loses its effectiveness with moderate- to low-ticket items.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
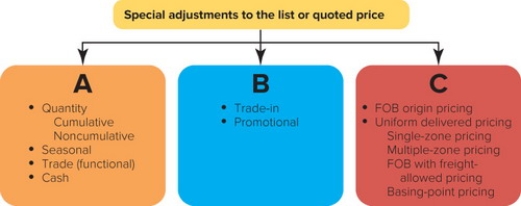 Figure 14-7
-Figure 14-7 above shows the three major types of special adjustments to the list or quoted price. Box A represents
Figure 14-7
-Figure 14-7 above shows the three major types of special adjustments to the list or quoted price. Box A represents
A) demand-oriented price adjustments.
B) allowances.
C) geographical adjustments.
D) discounts.
E) customary pricing adjustments.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
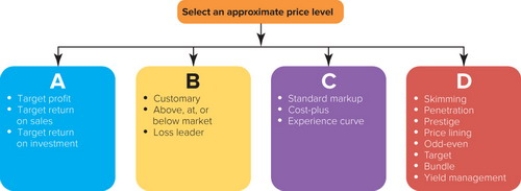 Figure 14-2
-Figure 14-2 above represents the four approaches to selecting an appropriate price level. Box B represents which approach?
Figure 14-2
-Figure 14-2 above represents the four approaches to selecting an appropriate price level. Box B represents which approach?
A) cost-oriented
B) profit-oriented
C) competition-oriented
D) demand-oriented
E) results-oriented
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Target pricing is considered to be a ________ approach to pricing.
A) cost-oriented
B) profit-oriented
C) demand-oriented
D) competition-oriented
E) service-oriented
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The first Apple iPhone was introduced in 2007 at an initial price of $600. People waited in line overnight so they could be one of the first to own this unique smartphone. Which pricing strategy did Apple use to help recoup its costs for developing the smartphone?
A) penetration pricing
B) experience-curve pricing
C) customary pricing
D) skimming pricing
E) target pricing
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Loss-leader pricing refers to
A) a pricing method where the price the seller charges is below the actual cost to make the product.
B) setting a low initial price and gradually but consistently increasing that price so as not to antagonize the consumer.
C) deliberately selling a product below its customary price, not to increase sales, but to attract customers' attention in hopes that they will buy other products as well.
D) a method of pricing based on a product's tradition, standardized channel of distribution, or other competitive factors.
E) pricing a product between 8 and 10% lower than nationally branded competitive products.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these businesses is most likely to use cost-plus-percentage-of-cost pricing?
A) real estate agency
B) insurance company
C) power company
D) space shuttle contractor
E) architect
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Experience-curve pricing refers to
A) the method of pricing where the price of a product often rises following the expansion of costs associated with the firm's producing and selling an increased volume of the product.
B) the point at which profits double, then double again, as more consumers buy the product.
C) a predictive pricing plan based upon the knowledge that the prices will fluctuate in a predictable pattern within a given industry based on the diffusion of innovation.
D) a method of pricing based on the learning effect, which holds that the unit cost of many products and services declines by 10 to 30 percent each time a firm's experience at producing and selling them doubles.
E) a pricing strategy that uses price estimates based upon the consensus of the salesforce and the firm's top management team.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A claim that a price is below a manufacturer's suggested or list price may be deceptive if
A) the items for sale had been purchased from another retailer.
B) the items for sale were part of a manufacturer's promotional allowance.
C) the items were part of a bulk order.
D) few or no sales occur at that price in a retailer's market area.
E) the items were purchased from the manufacturer at a higher price and the sale was part of a loss-leader promotion.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
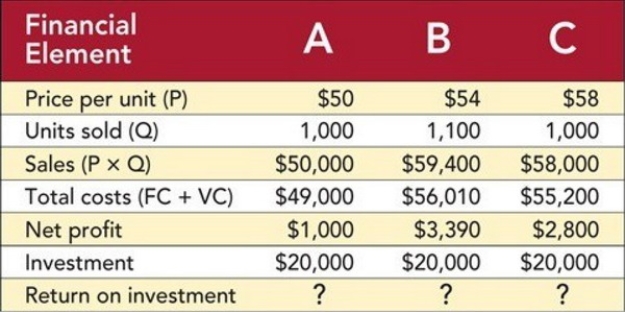 Figure 14-5
-Figure 14-5 above shows the results of a spreadsheet simulation to select a price to achieve a target return on investment (ROI) . What is the ROI for Scenario B?
Figure 14-5
-Figure 14-5 above shows the results of a spreadsheet simulation to select a price to achieve a target return on investment (ROI) . What is the ROI for Scenario B?
A) 2%
B) 5%
C) 10%
D) 14%
E) 17%
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The latest in appliance technology allows your refrigerator to send messages to your smartphone and even photos of the interior to remind you of what you need to pick up at the store. Taking advantage of strong consumer demand for technology-enabled products, marketers set prices for these refrigerators at thousands above other models. These marketers are using a ________ pricing strategy.
A) skimming
B) penetration
C) prestige
D) price lining
E) bundle
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Wrigley introduced a new flavor of Orbit brand sugar-free chewing gum, mint mojito, and its introductory price was low so that it quickly created loyal customers for the flavor. In this example, Wrigley used
A) skimming pricing.
B) price lining.
C) odd-even pricing.
D) penetration pricing.
E) loss-leader pricing.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mark Johnson, the manager of a discount consumer electronics store, was approached by the manufacturer's representative on behalf of a marketer of a popular and profitable line of storage racks. The manufacturer's representative implied that if Johnson didn't raise the retail prices for the storage racks to those paid by the marketer's nondiscount customers, Johnson's supply of racks would be severely curtailed. The manufacturer's representative is guilty of attempting
A) horizontal price fixing.
B) resale price maintenance.
C) price discrimination.
D) predatory pricing.
E) bait and switch pricing.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 319
Related Exams