A) variation in rates of evolutionary change among species.
B) homoplasy.
C) convergent evolution.
D) outgrouping.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
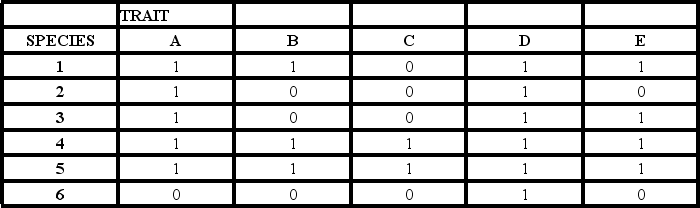 -The table shows the distribution of traits (A-E) in six extant species (1-6) .A "0" indicates the ancestral condition,and a "1" indicates the derived condition.Which pair of species shares the greatest number of derived characters (synapomorphies) ?
-The table shows the distribution of traits (A-E) in six extant species (1-6) .A "0" indicates the ancestral condition,and a "1" indicates the derived condition.Which pair of species shares the greatest number of derived characters (synapomorphies) ?
A) 4 and 5
B) 2 and 4
C) 1 and 4
D) 3 and 4
E) 2 and 5
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Characteristics that have arisen in organisms as a result of common evolutionary descent are said to be ________ characteristics.
A) homologous
B) homoplastic
C) adaptive
D) derived
E) ancestral
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The study and reconstruction of phylogenies is
A) evolution.
B) systematics.
C) taxonomy.
D) taxidermy.
E) cladistics.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A phylogenetically-based taxonomy is important not only in creating a logical way to name organisms,but also in learning about ________ of organisms using information in related species.Check all that apply.
A) physiology
B) behavior
C) development
D) morphology
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
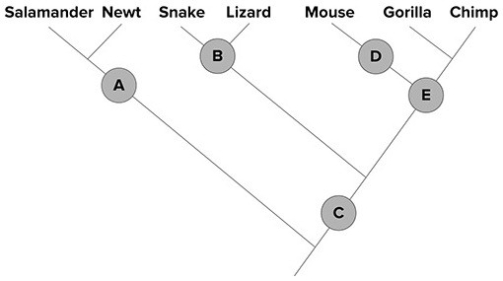 -A frog should be added to the phylogeny above at point
-A frog should be added to the phylogeny above at point
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
E) E.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Based on the phylogeny shown,choose the true statement about evolutionary relationships.
A) Ginkgo is more closely related to oak than rose.
B) Oak is equally related to rose and pine.
C) Fern is more closely related to pine than to rose.
D) Fern is equally related to ginkgo and oak.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Birds,snakes,lizards,turtles,and crocodiles are all thought to share a common ancestor and several homologous traits.Assuming that this is true,these groups of animals and their common ancestor would represent
A) a polyphyletic group.
B) a monophyletic group.
C) homoplastic convergence.
D) an outgroup.
E) a species cluster.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A group is considered monophyletic if
A) all members of the group share a common ancestor that is included in the group.
B) not all descendants of the common ancestor are included.
C) all members share homoplastic traits.
D) the group does not contain the most recent common ancestor.
E) it is the most parsimonious grouping.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The evolutionary sequence in the development of a complex character can be best analyzed through
A) homoplasies.
B) phylogenetics.
C) taxonomy.
D) classification.
E) synapomorphies.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the true statements about the evolution of larval dispersal in marine snails.
A) The evolution of non-dispersing snails is likely to hinder speciation.
B) Clades of non-dispersing snails are less species rich than those of dispersing snails.
C) Loss of structures in the transition from dispersing to non-dispersing may inhibit evolutionary reversal.
D) Possession of dispersing larvae is the ancestral state in snails.
E) Cladistics shows that there are more instances of the transition from dispersing to non-dispersing larvae than the reverse.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
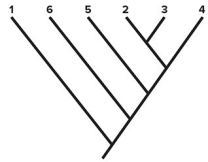 -Consider the cladogram shown.If we designate species 1 as the outgroup,which species has the greatest number of ancestral character states (pleisiomorphies) ?
-Consider the cladogram shown.If we designate species 1 as the outgroup,which species has the greatest number of ancestral character states (pleisiomorphies) ?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One day after a biology class four of your friends argue about the difference between phylogeny and systematics.Which friend is right?
A) Friend A states that systematics and phylogenies are really the same,one is more recent than the other,but basically they are the same.
B) Friend B says that systematics is the same as cladistics and cladistics is reconstructing clades,which ultimately lead to the development of phylogenies.
C) Friend C argues that systematics is the actual collecting and cataloguing of specimens into museums that can be used later by scientists to construct clades and phylogenies.
D) Friend D says that the way she remembers is that systematics is the reconstruction and study of phylogenies.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
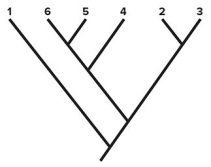 -Consider the cladogram shown.Based on this cladogram,which species has the greatest number of ancestral character states (pleisiomorphies) ?
-Consider the cladogram shown.Based on this cladogram,which species has the greatest number of ancestral character states (pleisiomorphies) ?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The common ancestor shared by mouse and gorilla is at point ________ on the phylogeny shown.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Derived character states shared by clade members are called
A) ancestral traits.
B) homoplasies.
C) synapomorphies.
D) plesiomorphies.
E) symplesiomorphies.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
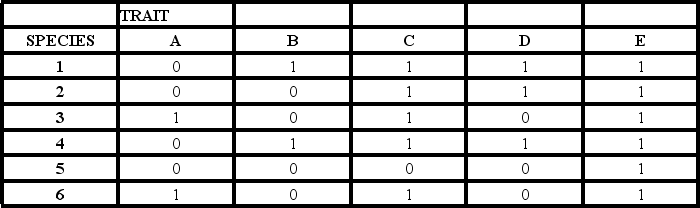 -The table shows the distribution of traits (A-E) in six extant species (1-6) .A "0" indicates the ancestral condition,and a "1" indicates the derived condition.Which species has the greatest number of ancestral character states (pleisiomorphies) ?
-The table shows the distribution of traits (A-E) in six extant species (1-6) .A "0" indicates the ancestral condition,and a "1" indicates the derived condition.Which species has the greatest number of ancestral character states (pleisiomorphies) ?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -The table shows the distribution of traits (A-E) in six extant species (1-6) .A "0" indicates the ancestral condition,and a "1" indicates the derived condition.Which trait is least informative of phylogenetic relationships within the group?
-The table shows the distribution of traits (A-E) in six extant species (1-6) .A "0" indicates the ancestral condition,and a "1" indicates the derived condition.Which trait is least informative of phylogenetic relationships within the group?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
A ________ group consists of the most recent common ancestor and some of its descendants.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure shows the evolution of HIV and SIV.Choose the true statements about the evolution of HIV (Select all that apply) . 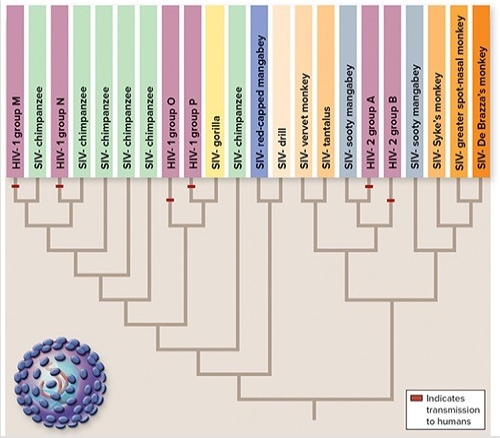
A) All strains of HIV are included within clades with SIV strains.
B) A strain of HIV is never more closely related to another strain of HIV than it is to a SIV strain.
C) Humans acquired different subtypes of HIV from different primate hosts.
D) HIV-1 group O is more closely related to SIV-chimpanzee than SIV-gorilla.
E) All strains of SIV are included within clades with HIV strains.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 67
Related Exams