A) the sum of all business income earned.
B) the sum of all consumer income earned.
C) all the spending on goods and services earned by consumer's income.
D) the sum of all incomes earned from production.
E) net of taxes.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following question(s) , suppose that an economy produces only bread and computers. Assume that all production is consumed in each year, and that price and quantity data are given in the table below.
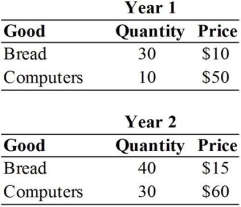 -If a particular measure of real GDP consistently underestimates growth in real GDP, then the rate of inflation as measured by the GDP deflator
-If a particular measure of real GDP consistently underestimates growth in real GDP, then the rate of inflation as measured by the GDP deflator
A) will consistently be overestimated.
B) will consistently be underestimated.
C) will be overestimated and underestimated equally often.
D) cannot be calculated.
E) is not a good predictor of the inflation rate in the CPI.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The participation rate equals
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
GDP may inaccurately measure the value of aggregate output because it may not properly account for
A) production in the underground economy and the true value of government production.
B) the true value of government production and the proper value of purchases and sales of used goods.
C) the proper value of purchases and sales of used goods and depreciation of consumer durables.
D) the depreciation of consumer durables and production in the underground economy.
E) all services produced.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following question(s) , suppose an economy produces only pens and pencils, and that the quantity and price data is given by this table:
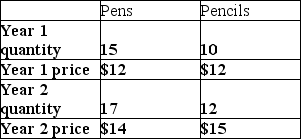 -What is the real GDP in year 1 using base year 2?
-What is the real GDP in year 1 using base year 2?
A) $418
B) $300
C) $360
D) $338
E) $294
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
National savings must equal
A) I + NX + NFP.
B) I - NX - NFP.
C) Y - NFP + C + G.
D) Yd - C.
E) T - TR - INT - G.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that GDP is equal to 1,000, national saving is equal to 200, the current account deficit is equal to 100, and the government budget deficit is equal to 50. Private savings must equal
A) 150.
B) 200.
C) 250.
D) 300.
E) 350.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When there is rapid inflation,
A) growth in nominal GDP exceeds growth in real GDP.
B) growth in real GDP exceeds growth in nominal GDP.
C) growth in real GDP and nominal GDP are roughly equal.
D) there can never be any growth in nominal GDP.
E) government tries to increase growth in real GDP.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Approaches to measuring GDP include
A) cost approach.
B) GDP approach.
C) income approach.
D) trade approach.
E) value-subtracted approach.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Intermediate goods are
A) irrelevant in the overall economy.
B) purchased by consumers.
C) goods that are produced and used as inputs into the production process.
D) sold to foreigners.
E) not a consumption good.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Real GDP values current production at
A) current year prices.
B) the best estimate of next year's prices.
C) the average of price levels over the entire sample period.
D) base year prices.
E) the purchase price not the asking prices of goods and services.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The income approach to calculating GDP includes
A) consumer spending.
B) exports of income earned.
C) net interest income.
D) government surpluses.
E) investment.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Jim's Nursery produces and sells $1,100 worth of flowers. Jim uses no intermediate inputs. He pays his workers $700 in wages, pays $100 in taxes and pays $200 in interest on a loan. Jim's profit is
A) $100.
B) $200.
C) $400.
D) $800.
E) $1,000.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Jim's Nursery produces and sells $1,100 worth of flowers. Jim uses no intermediate inputs. He pays his workers $700 in wages, pays $100 in taxes and pays $200 in interest on a loan. Jim's contribution to GDP is
A) $900.
B) $1,000.
C) $1,100.
D) $1,800.
E) $2,000.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Even when measured accurately, GDP may be a misleading measure of economic welfare because it cannot account for
A) the value of government spending and how efficiently we produce goods and services.
B) how efficiently we produce goods and services and the value of non-market production.
C) the value of non-market production and the consequences of an unequal distribution of income.
D) the consequences of an unequal distribution of income and the value of government spending.
E) the cost of intermediate goods and services.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following question(s) , suppose that an economy produces only bread and computers. Assume that all production is consumed in each year, and that price and quantity data are given in the table below.
 -Significant problems with measuring real GDP and the price level include
-Significant problems with measuring real GDP and the price level include
A) changes in the importance of intermediate goods.
B) purchases of used goods.
C) changes in the population size.
D) changes in the quality of goods over time.
E) changes in the size of the government.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following question(s) , suppose that an economy produces only bread and computers. Assume that all production is consumed in each year, and that price and quantity data are given in the table below.
 -When we try to measure real GDP and the price level, if we underestimate the growth in real GDP, we will
-When we try to measure real GDP and the price level, if we underestimate the growth in real GDP, we will
A) always underestimate the rate of inflation.
B) sometimes underestimate the rate of inflation.
C) always overestimate the rate of inflation.
D) sometimes overestimate the rate of inflation.
E) not be able to measure the rate of inflation.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Investment spending is
A) less volatile than consumption spending.
B) much more volatile than consumption spending.
C) equally as volatile as government spending.
D) equally volatile as GDP.
E) a larger fraction of GDP than consumption is.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Acme Steel Co. produces 1,000 tons of steel. Steel sells for $30 per ton. Acme pays wages of $10,000. Acme buys $15,000 worth of coal, which is needed to produce the steel. Acme pays $2,000 in taxes. Acme's profit is
A) $0.
B) $2,000.
C) $3,000.
D) $15,000.
E) $25,000.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Discouraged workers are
A) those who have given up looking for work, even though they would like to be employed.
B) those who quit working because they are dissatisfied with their jobs.
C) those who unmotivated workers who bring down a country's productivity.
D) those who would like to find a second job to supplement their income, but have not yet found one.
E) those who only work in the summer months.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 73
Related Exams